INDICATION
MENVEO is a vaccine indicated for active immunization to prevent invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups
MENVEO is a vaccine indicated for active immunization to prevent invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y, and W-135 in individuals 2 months through 55 years of age. MENVEO does not prevent N. meningitidis serogroup B infections.
MENVEO is a vaccine indicated for active immunization to prevent invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y, and W-135 in individuals 2 months through 55 years of age. MENVEO does not prevent N. meningitidis serogroup B infections.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR MENVEO
- Do not administer MENVEO to individuals with a severe allergic reaction (eg, anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of MENVEO, to any component of this vaccine, or to any other diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine
- Do not administer MENVEO to individuals with a severe allergic reaction (eg, anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of MENVEO, to any component of this vaccine, or to any other diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine
- Appropriate medical treatment must be available should an acute allergic reaction, including an anaphylactic reaction, occur following administration of MENVEO
- Syncope (fainting) has occurred in association with administration of MENVEO. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting
- Do not administer MENVEO to individuals with a severe allergic reaction (eg, anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of MENVEO, to any component of this vaccine, or to any other diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine
- Appropriate medical treatment must be available should an acute allergic reaction, including an anaphylactic reaction, occur following administration of MENVEO
- Syncope (fainting) has occurred in association with administration of MENVEO. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting
- Some individuals with altered immunocompetence, including some individuals receiving immunosuppressant therapy, may have reduced immune responses to MENVEO
- Individuals with certain complement deficiencies and individuals receiving treatment that inhibits terminal complement activation (for example, eculizumab) are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y, and W, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination with MENVEO
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has been reported in temporal relationship following administration of another US-licensed meningococcal quadrivalent polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. The decision to administer MENVEO to individuals with a history of GBS should take into account the expected benefits and potential risks
- Apnea following intramuscular vaccination has been observed in some infants born prematurely. A decision about when to administer MENVEO to an infant born prematurely should be based on consideration of the individual infant’s medical status and the potential benefits and possible risks of vaccination
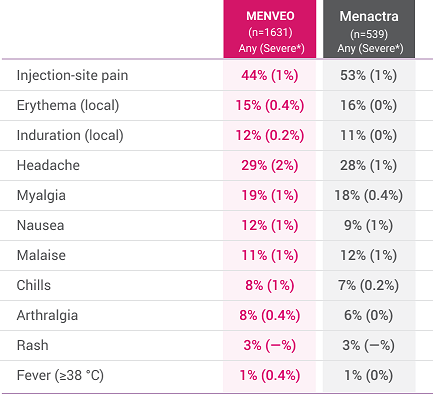
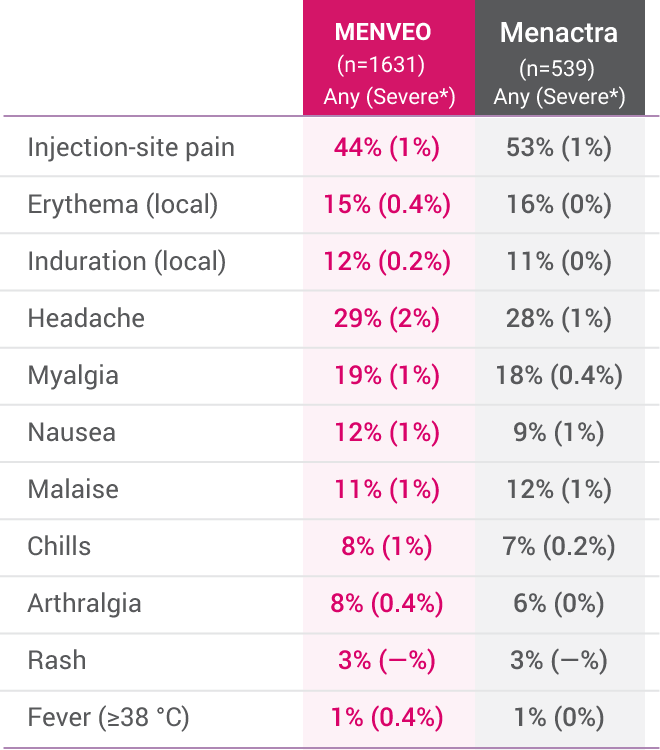
- Common solicited adverse reactions with MENVEO among children initiating vaccination: at 2 months of age and receiving the four-dose series were tenderness and erythema at injection site, irritability, sleepiness, persistent crying, change in eating habits, vomiting, and diarrhea; at 7 months through 23 months of age and receiving the two-dose series were tenderness and erythema at injection site, irritability, sleepiness, persistent crying, change in eating habits, and diarrhea; at 2 through 10 years of age who received MENVEO were injection site pain, erythema, irritability, induration, sleepiness, malaise, and headache. Common solicited adverse reactions among adolescents and adults aged 11 through 55 years who received a single dose of MENVEO were pain at the injection site, headache, myalgia, malaise, and nausea. Across all age groups, some events were severe. Similar rates of solicited adverse reactions among adolescents and adults were observed following a single booster dose
- In two clinical studies, there were no notable differences in frequency and severity of solicited adverse reactions in individuals who received MENVEO 1-vial presentation compared to individuals who received the 2-vial presentation
- Vaccination with MENVEO may not result in protection in all vaccine recipients
Please see full Prescribing Information for MENVEO.